Modelling and Estimation of Interior Orientation of Non-Metric Cameras using Artificial Intelligence
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51173/jt.v5i2.950Keywords:
Photogrammetry, Close Range Photogrammetry, Interior Orientation, Artificial IntelligenceAbstract
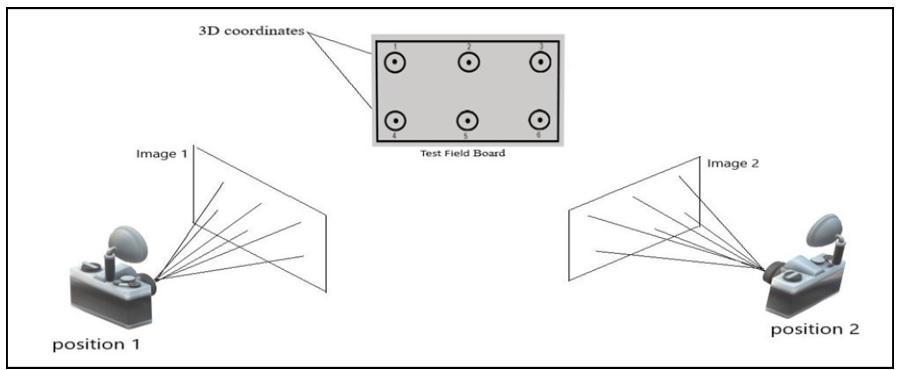
With the advancement of low-cost digital cameras and their widespread, especially in smartphones, these cameras are not designed for photogrammetry applications. The main aim of this study is to model and estimate the interior orientation parameters (IOPs) for images captured by volunteer-run cameras using artificial intelligence. These cameras were unavailable to perform traditional calibration processes or use images from unknown sources for image measuring. Estimating IOPs using random values within the range determined by testing the selected sample's consistency. Optimization was performed by Utilizing the Simulated Annealing algorithm based on stereo calibration to obtain the best possible values of these parameters that produce the minimum RMS-reprojection error attained. By The variance between the parameters from the pre-calibration process and estimated by an artificial intelligence system, The coefficient of determination in the IOPs (focal length R2 = 0.717 to 0.812, principal point (X, Y) R2 = (0.674 to 0.869, 0.504 to 0.613), Both radial and tangential coefficients, R2 was close to zero). Therefore, the estimations of radial distortions k1, k2, and tangential distortions p1 and p2 are invalid. A reasonably strong relationship between principal distance and principal point with low lens distortion parameters due to the significant relative differences between the distortion parameters, sufficient strength of the relationship between calculating parameters, and estimating according to accuracy tolerance in photogrammetry applications.
Downloads
References
Z. Zhang and Q. Tang, "Camera self-calibration based on multiple view images," in 2016 Nicograph International (NicoInt), 2016, pp. 88–91.
K. Jain, "How photogrammetric software works: A perspective based on UAV's exterior orientation parameters," J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens., vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 641–649, 2021.
R. A. Rutenbar, "Simulated annealing algorithms: An overview," IEEE Circuits Devices Mag., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 19–26, 1989.
C. S. Fraser, "Digital camera self-calibration," ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens., vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 149–159, 1997.
Z. Zhang, "A flexible new technique for camera calibration," IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 1330–1334, 2000.
L. Song, W. Wu, J. Guo, and X. Li, "Survey on camera calibration technique," in 2013 5th International conference on intelligent human-machine systems and cybernetics, 2013, vol. 2, pp. 389–392.
H. Brunken and C. Gühmann, "Deep learning self-calibration from planes," in Twelfth International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2019), 2020, vol. 11433, p. 114333L.
P. Bao, F. Gao, L. Shi, and S. Guo, "An Improved QPSO Algorithm Based on EXIF for Camera Self-calibration," in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), 2021, pp. 762–767.
D. Sims-Waterhouse, M. Isa, S. Piano, and R. Leach, "Uncertainty model for a traceable stereo-photogrammetry system," Precis. Eng., vol. 63, pp. 1–9, 2020.
W. Saif and A. Alshibani, "Smartphone-Based Photogrammetry Assessment in Comparison with a Compact Camera for Construction Management Applications," Appl. Sci., vol. 12, no. 3, p. 1053, 2022.
A. Ali and P. Smrz, "Camera auto-calibration for complex scenes," in Thirteenth International Conference on Machine Vision, 2021, vol. 11605, p. 116051W.
Y. Zhang, X. Zhao, and D. Qian, "Learning-Based Framework for Camera Calibration with Distortion Correction and High Precision Feature Detection," arXiv Prepr. arXiv2202.00158, 2022.
H. A. Ajjah, "GitHub - hasanain2020a/Interior-orientation-by-heuristics: Modeling and Estimation Interior Orientation of Non-Metric Cameras using Artificial Intelligence." https://github.com/hasanain2020a/Interior-orientation-by-heuristics (accessed Oct. 12, 2022).
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Hasanain A. Ajjah, Ahmed H H Alboabidallah, Mamoun U. Mohammed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
















