An Efficiency Optimized Direct Model Predictive Control of Induction Machine Drive
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51173/jt.v6i3.2598Keywords:
Induction Machines, PI Controller, Direct Model Predictive Control, Cost Function Minimization, State VariablesAbstract
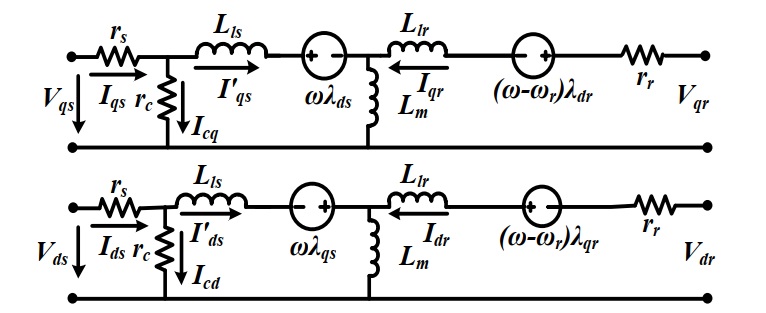
Presented in this paper is a direct model predictive control (MPC) for directly controlling the rotor speed and flux of an inverter-fed induction motor, which is also applicable to induction generators. Discrete dynamic model of the induction machine is applied in stationary reference frame with pre-set present and past reference values of the speed and rotor flux for generating the stator current references The uniqueness of the MPC proposed herein is that it does not require outer cascade proportional plus integral (PI) controllers used for regulating rotor speed and flux. Elimination of the outer loop cascade is made possible in this article by the introduction of a unique four-term cost function comprising of weighted magnitudes of the errors between four measured state variables and their reference commands. The four state variables in the unique cost function are the rotor speed, the rotor flux linkage, quadrature axis and direct axis stator currents. The MPC minimizes the cost function at every switching instance by selecting the switching states that gives the least cost function. Consequently, the selected optimal switching states are used to switch optimal inverter output voltages across the machine’s stator terminals. As a precursor for obtaining an optimal rotor flux command in the MPC for every torque output, another unique efficiency improvement scheme is developed, which uniquely determines the stator angular velocity and the rotor flux that minimizes the core and copper losses while maintaining a constant slip operation. Therefore, efficacy of the proposed direct model predictive control scheme is verified by comparing its results to results obtained from equivalent vector control on equivalent machine. Results presented show lower loss regime with MPC on optimal stator angular velocity and rotor flux than vector control.
Downloads
References
C. A. Rojas, J. Rodriguez, F. Villarroel, J. R. Espinoza, C. A. Silva, and M.Trincado, “Predictive torque and flux control without weighting factors,” IEEE Transaction on Industrial Electronics, vol. 60, no. 2, pp. 681–690, Feb. 2013. DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2012.2206344.
P. Šimek, and V. Valouch, “Generalized predictive power control for grid-connected converter,” International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, vol. 125, 106380, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2020.106380.
Y. Zhang, and H. Yang, “Model-Predictive Flux Control of Induction Motor Drives with Switching Instant Optimization” IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 30, no. 3, September 2015. DOI: 10.1109/TEC.2015.2423692.
E. Santana, E. Bim, and W. Amaral, “A Predictive Algorithm for Controlling Speed and Rotor Flux of Induction Motor” IEEE Transactions On Industrial Electronics, vol. 55, no. 12, December 2008. DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2008.2007376.
H. Miranda, P. Cortés, J. I. Yuz, and J. Rodríguez, “Predictive Torque Control of Induction Machines Based on State-Space Models” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 56, no. 6, June 2009 DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2014904.
S. Agoro, A. Balogun, O. Ojo and F. Okafor, "Direct Model-Based Predictive Control of a Three-Phase Grid Connected VSI for Photovoltaic Power Evacuation," 2018 9th IEEE International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Charlotte, NC, USA, 2018, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/PEDG.2018.8447817.
Y. Zhou, H. Li , and H. Zhang. “Model-free deadbeat predictive current control of a surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor drive system”, Journal of Power Electronics. vol. 18, no 1, pp. 103-15. 2018 DOI: 10.6113/JPE.2018.18.1.103.
J. Mao, H. Li, L. Yang, H. Zhang, L. Liu, X. Wang and J. Tao, "Non-cascaded model-free predictive speed control of SMPMSM drive system," IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 153-162, 2021. DOI: 10.1109/TEC.2021.3090427.
L. Yang, H. Li, J. Huang, Z. Zhang and H. Zhao, "Model predictive direct speed control with novel cost function for SMPMSM drives," IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 37, no. 8, pp. 9586--9595, 2022. DOI: 10.1109/TPEL.2022.3155465
M. Liu, K.W. Chan, J. Hu, W. Xu, and J. Rodriguez . “Model predictive direct speed control with torque oscillation reduction for PMSM drives”, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 4944-56. Feb. 2019 DOI: 10.1109/TII.2019.2898004.
X. Zhang, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhao, and Y. He, “Robust model predictive direct speed control for SPMSM drives based on full parameter disturbances and load observer,” IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 35, no. 8, pp. 8361-73. Dec. 2019 DOI: 10.1109/TPEL.2019.2962857.
C. Gong, Y. Hu, K. Ni, J. Liu and J. Gao, "SM Load Torque Observer-Based FCS-MPDSC With Single Prediction Horizon for High Dynamics of Surface-Mounted PMSM," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 20-24, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2019.2929714.
A. R. Munoz, T.A. Lipo, “Complex vector model of the squirrel-cage induction machine including instantaneous rotor bar currents,” IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1332 – 1340, Dec. 1999 DOI: 10.1109/28.806047.
Y.A. Zorgani, Y. Koubaa, and M. Boussak, "MRAS state estimator for speed sensorless ISFOC induction motor drives with Luenberger load torque estimation," ISA transactions, 61, pp. 308-317. 2016 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2015.12.015.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Adeola Balogun, Sodiq Agoro, Sunday Adetona, Ayobami Olajube, Frank Okafor

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
















