A Study into the Electrochemical Behavior of Nano Antibiotics as A Promising Treatment for Helicobacter Pylori Infection by Cyclic Voltammetry
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51173/jt.v4i33.548Keywords:
Amoxicillin NPs, Azithromycin NPs, Cyclic Voltammetry FESEM, H-pylori infection, Metronidazole NPs, Nano-kit, Serum Blood SamplesAbstract
The helicobacter-pylori (H.pylori) bacteria that infects the digestive system is one of the bacteria that is intractable in routine treatments with antibiotics, as it has been studied using nano-antibiotics studied by the electrochemical behavior of three Nano antibiotics.
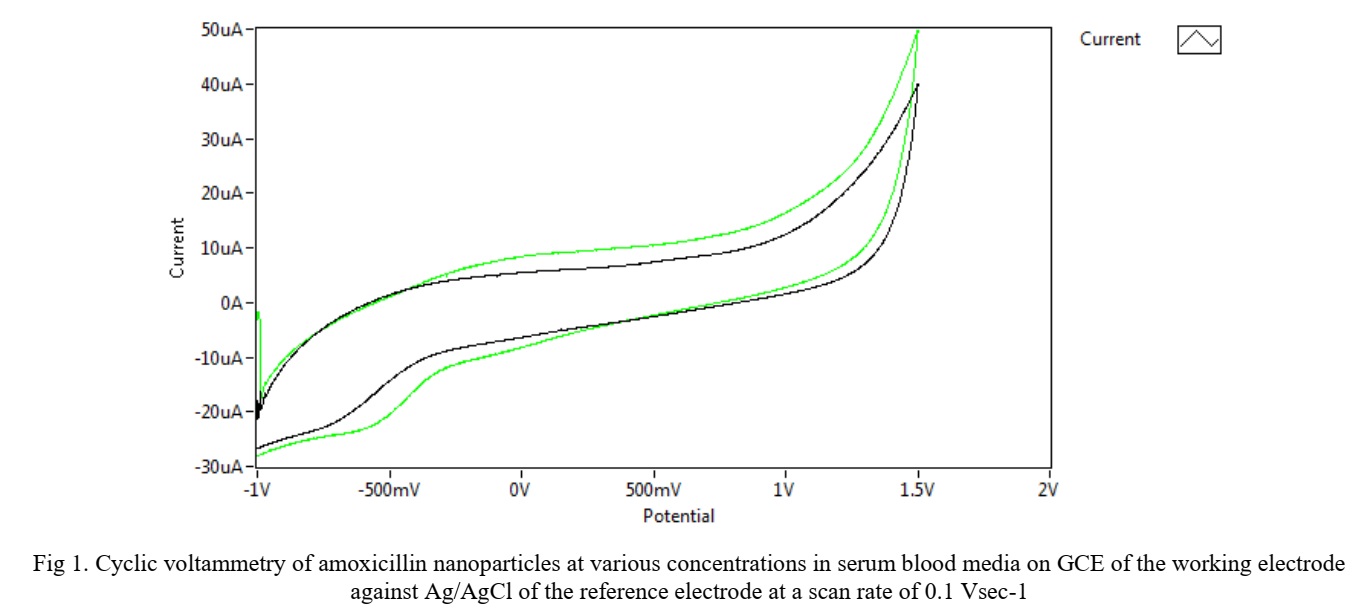
The study aims to identify the extent of the effect of micro-antibiotics on the composition of the blood serum medium by electrochemical analysis using the cyclic voltammetric method and to compare it with nano-antibiotics.
Three Nano-antibiotics such as Amoxicillin NPs, Azithromycin NPs, and Metronidazole NPs, and the mixture of the three nanoparticles as Nano-Kit were investigated in blood serum medium utilizing cyclic voltammetry methods by a glass carbonic electrode (GCE). The three nanoparticles in antibiotics were prepared by converting the micro antibiotic with a lyophilizer technique and characterization by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) with all antibiotics in Nano size.
The results showed that all Nano compounds act as an antioxidant antibiotic in the blood serum medium. The study also included the electrochemical characterization of the Nano-kit of the mixture for the three Nano-biotics to prove anti-oxidative stress. It was found that the three nano-biotics have reduced current peaks without any oxidation peaks.
The three nano-antibiotics can be an excellent treatment to eradicate H. pylori infection permanently. Therefore, the results of this research can be adapted to use the nano-kit of the mixture in the appropriate treatment of H.pylori infection.
Downloads
References
M. M. Radhi, H. N. Abdullah, S. A. Al-Asadi, and E. A. J. Al-Mulla, "Electrochemical oxidation effect of ascorbic acid on mercury ions in blood sample using cyclic voltammetry," International Journal of Industrial Chemistry, vol. 6, pp. 311-316, 2015.
M. M. Radhi, H. N. Abdullah, M. S. Jabir, and E. A. J. Al-Mulla, "Electrochemical effect of ascorbic acid on redox current peaks of CoCl2 in blood medium," Nano Biomed. Eng, vol. 9, pp. 103-106, 2017.
M. M. Radhi and E. A. J. Al-Mulla, "Use of a grafted polymer electrode to study mercury ions by cyclic voltammetry," Research on Chemical Intermediates, vol. 41, pp. 1413-1420, 2015.
M. M. Radhi, F. K. M. Alosfur, and N. J. Ridha, "Voltammetric characterization of grafted polymer modified with ZnO nanoparticles on glassy carbon electrode," Russian journal of electrochemistry, vol. 54, pp. 27-32, 2018.
M. M. Radhi, M. A. A. Alasady, and M. S. Jabir, "Electrochemical Oxidation effect of nicotine in cigarette tobacco on a blood medium mediated by GCE using cyclic voltammetry," Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta, vol. 38, pp. 139-148, 2020.
L. Santacroce, M. Di Cosola, L. Bottalico, S. Topi, I. A. Charitos, A. Ballini, et al., "Focus on HPV infection and the molecular mechanisms of oral carcinogenesis," Viruses, vol. 13, p. 559, 2021.
F. Mégraud and P. Lehours, "Helicobacter pylori detection and antimicrobial susceptibility testing," Clinical microbiology reviews, vol. 20, pp. 280-322, 2007.
Q. Wang, Q. Xue, T. Chen, J. Li, Y. Liu, X. Shan, et al., "Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for antibiotics and their applications," Chinese Chemical Letters, vol. 32, pp. 609-619, 2021.
R. Grande, F. Sisto, V. Puca, S. Carradori, M. Ronci, A. Aceto, et al., "Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of new synthesized silver ultra-nanoclusters (SUNCs) against Helicobacter pylori," Frontiers in microbiology, vol. 11, p. 1705, 2020.
I. A. Cardos, D. C. Zaha, R. K. Sindhu, and S. Cavalu, "Revisiting therapeutic strategies for H. pylori treatment in the context of antibiotic resistance: focus on alternative and complementary therapies," Molecules, vol. 26, p. 6078, 2021.
T. Wu, L. Wang, M. Gong, Y. Lin, Y. Xu, L. Ye, et al., "Synergistic effects of nanoparticle heating and amoxicillin on H. pylori inhibition," Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, vol. 485, pp. 95-104, 2019.
N. Alsaiari, K. Katubi, F. Alzahrani, S. Siddeeg, and M. Tahoon, "The Application of Nanomaterials for the Electrochemical Detection of Antibiotics: A Review. Micromachines 2021, 12, 308," ed: s Note: MDPI stays neu-tral with regard to jurisdictional claims in …, 2021.
N. S. Alsaiari, K. M. M. Katubi, F. M. Alzahrani, S. M. Siddeeg, and M. A. Tahoon, "The application of nanomaterials for the electrochemical detection of antibiotics: A review," Micromachines, vol. 12, p. 308, 2021.
M. M. RADHI, Z. N. HAMAD, M. S. JABIR, and S. Sabah, "Electrochemical Study Of Nitrofurantoin At Micro-And Nanoparticles In Blood Medium Using Cyclic Voltammetric."
H. Sardarabadi, M. Mashreghi, K. Jamialahmadi, and T. Dianat, "Resistance of nanobacteria isolated from urinary and kidney stones to broad-spectrum antibiotics," Iranian journal of microbiology, vol. 6, p. 230, 2014.
M. Azhdarzadeh, F. Lotfipour, P. Zakeri-Milani, G. Mohammadi, and H. Valizadeh, "Anti-bacterial performance of azithromycin nanoparticles as colloidal drug delivery system against different gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria," Advanced pharmaceutical bulletin, vol. 2, p. 17, 2012.
W. Gao, S. Thamphiwatana, P. Angsantikul, and L. Zhang, "Nanoparticle approaches against bacterial infections," Wiley interdisciplinary reviews: nanomedicine and nanobiotechnology, vol. 6, pp. 532-547, 2014.
E. Güncüm, T. Bakırel, C. Anlaş, H. Ekici, and N. Işıklan, "Novel amoxicillin nanoparticles formulated as sustained release delivery system for poultry use," Journal of veterinary pharmacology and therapeutics, vol. 41, pp. 588-598, 2018.
A. Elzatahry and M. M. Eldin, "Preparation and characterization of metronidazole‐loaded chitosan nanoparticles for drug delivery application," Polymers for Advanced Technologies, vol. 19, pp. 1787-1791, 2008.
R. Fateh, A. Javadi, J. Kardan-Yamch, H. A. Rahdar, M. Amini, F. Ghasemi, et al., "Construction of metronidazole capped in gold nanoparticles against Helicobacter pylori: antimicrobial activity improvement," Folia medica, vol. 63, pp. 197-202, 2021.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Sarah Abbas Hussein Al-saeed, Muhammed Mizher Radhi, Zuhair Numan Hamed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
















