Interpreting Myocardial Enzymatic Biomarkers in the Setting of Acute Myocardial Infraction AMI
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51173/jt.v4i4.782Keywords:
Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI), Myoglobin, Creatinine Kinas (CK), Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), Troponin T (TnT)Abstract
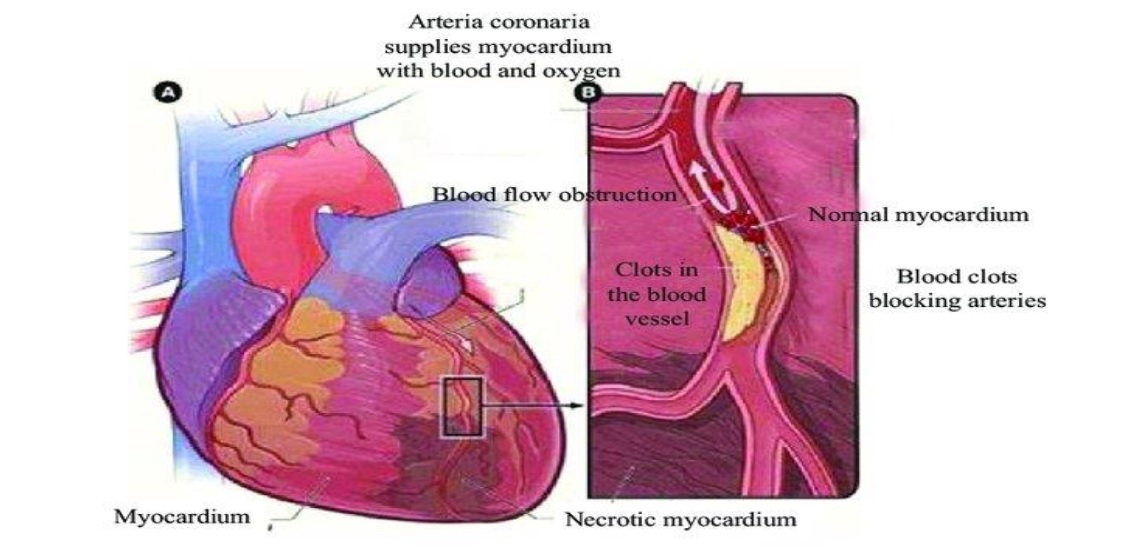
The rates of morbidity and mortality for acute myocardial infarction (AMI) have been rising quickly in the last few years. In the systemic circulatory loop, the heart normally pumps blood to the body's extremities. Cardiovascular disease, however, results from any heart function problem. The most fatal diseases in the world are known to be those involving the cardiovascular system. Over the past decade, biochemical marker testing are an important step in the diagnosis, and management of heart failure and in lowering one's risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Early diagnosis is paramount to choosing a clear and effective treatment strategy. Cardiac biomarkers are another effective method for classifying myocardial injury. The myocardial enzymatic biomarkers, also known as myocardial necrosis biomarkers, were among the various biomarkers that were initially studied. This review aims to allow for appropriate management steps to be initiated and more efficient and effective utilization of healthcare resources.
Downloads
References
Reindl M, Reinstadler SJ, Feistritzer HJ, et al. Acute myocardial infarction as a manifestation of systemic vasculitis. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016; 128(21-22):841–843.
Haasenritter J, Stanze D, Widera G, et al. Does the patient with chest pain have coronary heart disease? Diagnostic value of single symptoms and signs--a meta-analysis. Croat Med J. 2012;53(5):432–441.
Liakos M, Parikh PB. Gender disparities in presentation, management, and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018; 20(8):64.
Aydin S, Aydin S. Irisin concentrations as a myocardial biomarker. In: Patel VB, Preedy VR, editors. Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease. Dordrecht: Springer; 2016. pp. 489–504.
G. Yao et al. Comparative study of ticagrelor and clopidogrel in therapeutic effect of acute myocardial infarction patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 2017; 24: 1818–1820.
J. Boeddinghaus, T. Reichlin, T. Nestelberger, et al., "Early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in patients with mild elevations of cardiac troponin," Clinical Research in Cardiology. 2017; 106(6): 457–467, 2017.
Chaulin, Aleksey M., Duplyakov, Dmitry V. Biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction: diagnostic and prognostic value. Journal of Clinical Practice. 2020; 11(3): 75-84.
Yuqi Chen, Yifei Tao, Lan Zhang, Weiting Xu, Xiang Zhou. Diagnostic and prognostic value of biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. Postgrad Med J 2019;95:210–216.
Rachel Jacob and Mahmood Khan: Cardiac Biomarkers: What Is and What Can Be, Indian J Cardiovasc Dis Women-WINCARS 2018;3:240–244.
McLeish MJ, Kenyon GL. Relating structure to mechanism in creatine kinase. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;40(1):1–20.
Bong SM, Moon JH, Nam KH, Lee KS, Chi YM, Hwang KY. Structural studies of human brain-type creatine kinase complexed with the ADP-Mg2+-NO3- -creatine transition-state analogue complex". FEBS Letters.2008, 582 (28): 3959–65. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.10.039. PMID 18977227.
Wallimann T, WKnudsen J, Steenstrup B, Byrjalsen I, Hildebrandt P, Sørensen S. At what level of serum total creatine kinase activity can measurement of serum creatine kinase MB isoenzyme activity be omitted in suspected myocardial infarction? Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1989;49(7):661–665.
Kim S, Um TH, Cho CR, Jeon JS. False-positive elevation of creatine kinase MB mass concentrations caused by macromolecules in a patient who underwent nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Ann Lab Med. 2014;34(5):405–407.
N. Kume, H. Mit-suoka, K. Hayashida and M. Tanaka, “Pentraxin 3 as a Biomarker for Acute Coronary Syndrome: Comparison with Biomarkers for Cardiac Damage,” Journal of Cardiology, Vol. 58, No. 1, 2011, pp. 38-45. doi:10.1016/j.jjcc.2011.03.006.
Nicola J.Kluger MB and ChBMalcolm E.LeggetMD. Emerging Biomarkers in Acute Coronary Syndromes. A Pathophysiologic Perspective. 2022; 31(6): 779-786.
Suleyman Aydin, Kader Ugur, Suna Aydin, et al. Biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction: current perspectives. Vascular Health and Risk Management. 2019; 15:1-10.
Korff S, Katus HA, Giannitsis E. Differential diagnosis of elevated troponins. Heart. 2006;92(7):987–993.
Peacock WF, Baumann BM, Bruton D., et al. Efficacy of high-sensitivity troponin T in identifying very-low-risk patients with possible acute coronary syndrome. JAMA Cardiol 2018;3(2):104–111.
Aydin S, Aydin S. Irisin concentrations as a myocardial biomarker. In: Patel VB, Preedy VR, editors. Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease. Dordrecht: Springer. 2016;489–504.
Holmes RS., Goldberg E. Computational analyses of mammalian lactate dehydrogenases: human, mouse, opossum and platypus LDHs. Computational Biology and Chemistry.2009, 33 (5): 379–85. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2009.07.006. PMC
Heinova D, Rosival I, Avidar Y, Bogin E. Lactate dehydrogenaseisoenzyme distribution and patterns in chicken organs. Res Vet Sci.1999;67(3):309–312.
Livanova NB., Chebotareva NA., Eronina TB., Kurganov BI. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate as a catalytic and conformational cofactor of muscle glycogen phosphorylase B. Biochemistry. Biokhimiia. 2002; 67 (10): 1089–98. doi:10.1023/A:1020978825802.
Lippi G, Montagnana M, Salvagno GL, Guidi GC. Potential value for new diagnostic markers in the early recognition of acute coronary syndromes. CJEM. 2006;8:27–31.
Neelima S., Vedika R., Roshan K., and Puneet R. Glycogen Phosphorylase BB: A more Sensitive and Specific Marker than Other Cardiac Markers for Early Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2018 Jul; 33(3): 356–360. Published online 2017 Aug 3. doi: 10.1007/s12291-017-0685-y.
Khan IA, Wattanasuwan N. Role of biochemical markers in diagnosis of myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2005;104(2):238–240.
Wu AH, Apple FS, Gibler WB, Jesse RL, Warshaw MM, Valdes R. National academy of clinical biochemistry standards of laboratory practice: recommendations for the use of cardiac markers in coronary Clin Chem; 1999 Jul;45(7):1104-21.
Sheref A., Ahmed K, Debvarsha M, Mounika V, Ahmed E, Tamam M.Copeptin plus troponin in the rapid rule out of acute myocardial infarction and prognostic value on post-myocardial infarction outcomes: a systematic review and diagnostic accuracy study. Heart Vessels, 2022; 6. doi: 10.1007/s00380-022-02123-x.
Richard O., Saadu H. and Chinanu L.Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Diagnosis; Impact of Technology in Developing Highly Sensitive Biomarkers and Assays. Cardiology and Angiology. 2022; 11(4): 124-134.
Westermann D, Neumann JT, Sörensen NA, Blankenberg S. High-sensitivity assays for troponin in patients with cardiac disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2017;14(8):472–483.
Peacock WF, Baumann BM, Bruton D, et al. Efficacy of high-sensitivity troponin T in identifying very-low-risk patients with possible acute coronary syndrome. JAMA Cardiol. 2018; 3(2):104–111.
Shah AS, McAllister DA, Mills R, et al. Sensitive troponin assay and the classification of myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2015;128(5): 493–501.
Neumann JT, Sörensen NA, Ojeda F, et al. Early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction using high-sensitivity troponin I. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0174288.
Yader Sandoval, Bradley R. Lewis, Ramila A. Mehta, Olatunde O., Jonathan D. Knott. Rapid Exclusion of Acute Myocardial Injury and Infarction With a Single High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T in the Emergency Department: A Multicenter United States Evaluation. Circulation. 2022;1.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Khawla A. Kasar, Maha H. Al-Bahrani, Ahmed A. Mohsin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
















