Automated Computer Vision System for Urine Color Detection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51173/jt.v5i1.896Keywords:
Urine Color Detection, Images Processing, Machine Learning, Random Forest, Graphical User InterfaceAbstract
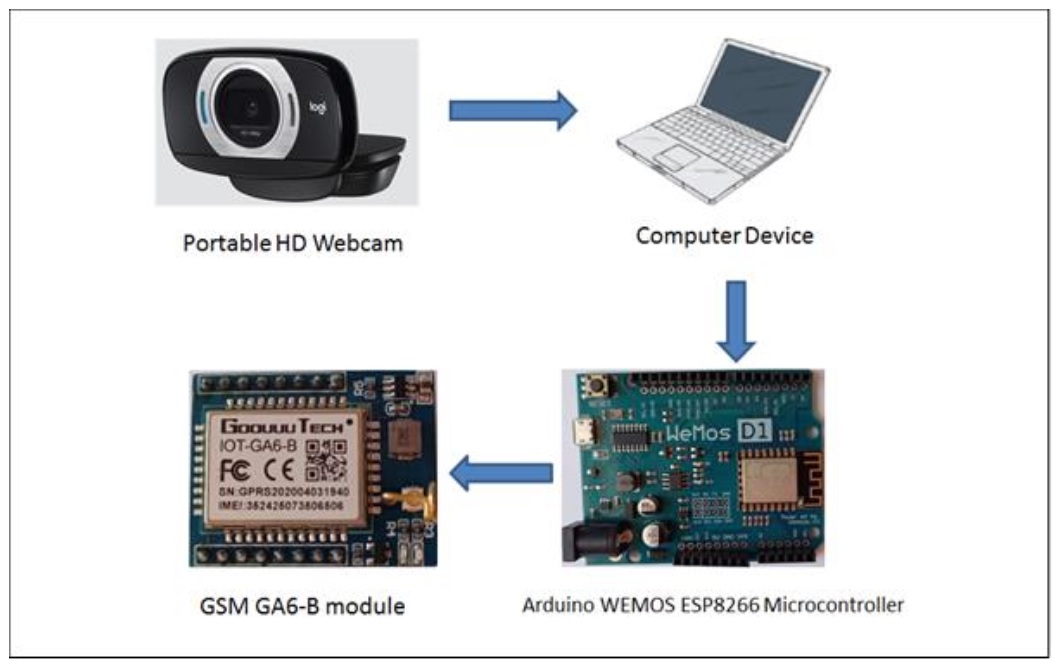
Urine color analysis is one of the most helpful indicators of health status, and any changes in urine color might be a symptom of serious disease, dehydration of the body, or caused by drugs. To get better assistance for urine color detection in the proposed system, a urine color automatic identification has been developed based on computer vision. The proposed system uses a web camera to capture an image in real-time, analyze it, and then classify the color of urine by using the random forest (RF) algorithm and show the result via the Graphical User Interface (GUI). In addition, the proposed system can send the results to the mobile phone of the patient or care provider by using an Arduino microcontroller and GSM module. Moreover, sending a voice message about the color of urine is related to pathological conditions. The results showed that the proposed system has high accuracy (approximately about 97%) in detecting urine color under different light conditions, with low cost, short time, and easy implementation. In the comparison with the current methods the proposed system has maximum accuracy and minimum error rate. This methodology can pave the way for an additional case study in medical applications, particularly in diagnosis, and patient health monitoring.
Downloads
References
A. J. Callens and J. W. Bartges, “Urinalysis,” Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract., vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 621–637, 2015.
A. K. Israni and B. L. Kasiske, “Laboratory assessment of kidney disease: glomerular filtration rate, urinalysis, and proteinuria,” Brenner and Rector’s The Kidney, vol. 9, pp. 1585–1619, 2011.
S. Demirdas and C. H. Schröder, “An infant with orange-colored urine,” Pediatr. Nephrol., vol. 25, no. 2, p. 381, 2010.
G. F. Cope and R. Whitfield, “Urine color testing and isoniazid monitoring,” Chest, vol. 124, no. 6, p. 2405, 2003.
N. K. Singh and N. Mirza, “Elderly woman with orange urine and purple hands,” in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 2008, vol. 83, no. 7, p. 744.
J. Floege, R. J. Johnson, and J. Feehally, Comprehensive clinical nephrology E-book. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2010.
M. Gulseth, “Patient education needs,” Manag. Anticoagulation Patients Hosp. Inpatient Anticoagulation Serv. Bethesda, MD, ASHP, pp. 101–122, 2007.
D. Basu, N. Painuly, and M. Sahoo, “Allergic to all medicines and red coloured urine,” 2008.
S. Y. Chan and D. Evans, “Red urine in a returning traveller,” Int. J. STD AIDS, vol. 16, no. 11, pp. 770–771, 2005.
J. S. Bryant and M. Gausche-Hill, “When is red urine not hematuria?: A case report,” J. Emerg. Med., vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 55–57, 2007.
K. L. Hon and K. L. Cheung, "Pink toes and red urine: what is this poison?" Hong Kong Med. journal= Xianggang yi xue za zhi, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 411–412, 2010.
C. Q. Edwards, “Anemia and the liver: hepatobiliary manifestations of anemia,” Clin. Liver Dis., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 891–907, 2002.
S. K. Ghosh, D. Bandyopadhyay, and S. Haldar, “Red urine and photosensitive skin rash: not only was our patient’s urine red, but his teeth had a reddish hue, as well,” J. Fam. Pract., vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 200–203, 2009.
R. M. Hsu and L. B. Baskin, “Laboratory evaluation of discolored urine. When is it hematuria?,” MLO. Med. Lab. Obs., vol. 32, no. 7, pp. 44–52, 2000.
C. Hallermann and H. J. Schulze, "Diffuse brown discoloration of skin, mucosa, and urine," Hautarzt., vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 51–53, 2011.
G. B. Fogazzi, The urinary sediment. An integrated view. Penerbit Buku Kompas, 2010.
P. Leclercq, C. Loly, P. Delanaye, C. Garweg, and B. Lambermont, “Green urine,” Lancet, vol. 373, no. 9673, p. 1462, 2009.
K. A. Tønseth, T. T. Tindholdt, B. M. Hokland, and F. E. Åbyholm, “Green urine after surgical treatment of pressure ulcer,” Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Hand Surg., vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 39–41, 2007.
B. D. Ku, K. C. Park, and S. S. Yoon, “Dark green discoloration of the urine after prolonged propofol infusion: a case report,” J. Clin. Pharm. Ther., vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 734–736, 2011.
F. Pak, “Green urine: an association with metoclopramide,” Nephrol. Dial. Transplant., vol. 19, no. 10, p. 2677, 2004.
C.-W. Lam and S. Y. Wong, “A case of green urine due to a traditional Chinese medicine containing methylene blue,” NZ Med J, vol. 123, no. 1312, pp. 71–76, 2010.
M. Vera, A. Molano, and P. Rodríguez, “Turbid white urine,” NDT Plus, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 45–47, 2010.
B. H. Eisner, C. Tanrikut, and D. M. Dahl, “Chyluria secondary to lymphorenal fistula,” Kidney Int., vol. 76, no. 1, p. 126, 2009.
K. B. Horner and D. J. Sas, “White urine in an asymptomatic child,” J. Pediatr., vol. 159, no. 2, p. 351, 2011.
R. D. Aycock and D. A. Kass, “Abnormal urine color.,” South. Med. J., vol. 105, no. 1, pp. 43–47, 2012.
C. C. Hortinela, J. R. Balbin, J. C. Fausto, and K. K. Viray, “Identification of crystals present in a urine sediment based on adaptive boosting algorithm,” in 2019 IEEE 11th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment, and Management (HNICEM), pp. 1–4.
A. Mathaweesansurn, S. Thongrod, P. Khongkaew, C. M. Phechkrajang, P. Wilairat, and N. Choengchan, “Simple and fast fabrication of microfluidic paper-based analytical device by contact stamping for multiple-point standard addition assay: Application to direct analysis of urinary creatinine,” Talanta, vol. 210, p. 120675, 2020.
J. Wu, M. Dong, C. Zhang, Y. Wang, M. Xie, and Y. Chen, “Magnetic lateral flow strip for the detection of cocaine in urine by naked eyes and smart phone camera,” Sensors, vol. 17, no. 6, p. 1286, 2017.
U. M. Jalal, G. J. Jin, and J. S. Shim, “Paper–plastic hybrid microfluidic device for smartphone-based colorimetric analysis of urine,” Anal. Chem., vol. 89, no. 24, pp. 13160–13166, 2017.
C. G. Ravazzi, M. de O. K. Franco, M. C. R. Vieira, and W. T. Suarez, “Smartphone application for captopril determination in dosage forms and synthetic urine employing digital imaging,” Talanta, vol. 189, pp. 339–344, 2018.
G. Budianto, T. Harsono, and H. Yuniarti, “Strip test analysis using image processing for diagnosing diabetes and kidney stone based on smartphone,” in 2018 International Electronics Symposium on Knowledge Creation and Intelligent Computing (IES-KCIC), 2018, pp. 235–241.
J. C. Dela Cruz, R. G. Garcia, M. I. D. Avilledo, J. C. M. Buera, R. V. S. Chan, and P. G. T. Espana, “Microscopic image analysis and counting of red blood cells and white blood cells in a urine sample,” in Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology, 2019, pp. 113–118.
T.-T. Wang et al., “A feasible image-based colorimetric assay using a smartphone RGB camera for point-of-care monitoring of diabetes,” Talanta, vol. 206, p. 120211, 2020.
I. Lewińska, M. Speichert, M. Granica, and Ł. Tymecki, “Colorimetric point-of-care paper-based sensors for urinary creatinine with smartphone readout,” Sensors Actuators B Chem., vol. 340, p. 129915, 2021.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ban Shamil Abdulwahed, Ali Al-Naji , Izzat Al-Rayahi , Ammar Yahya, Asanka G. Perera

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
















