Evaluation of Water Quality at the Confluence Region of Diyala and Tigris Rivers Based on the Weighted Arithmetic Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51173/jt.v5i1.1088Keywords:
Baghdad, Drinking, Diyala, Tigris, WQIAbstract
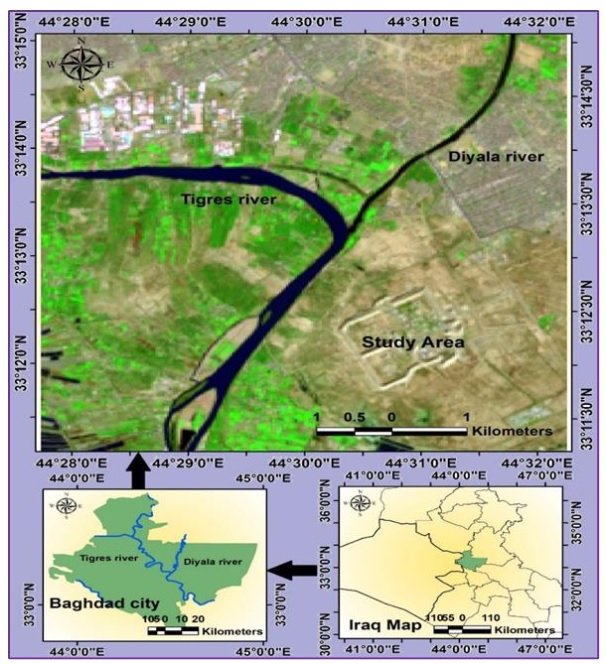
This study is conducted to assess the water quality index (WQI) of the Diyala and Tigris River confluence region south of Baghdad (Al-Tuwaitha), based on the Weighted Arithmetic method. Sixteen samples of water were collected from different location in the region through two periods 5/11/2021 and 13/3/2022. Water quality parameters such as (PH, EC, TDS, TH, Ca, Mg, Cl, Turbidity, ALK, SO4, HCO3, Na, and K) were used to evaluate WQI in the study area.
The final results showed that the water was not suitable for drinking due to the high concentration of water quality parameters. In the 5 November 2021, the water quality in the study area was classified into (good, poor, very poor, and polluted) where the percentages of the above classes were 4%, 6%, 39%, and 51% respectively, while the percentages for the season 13thMarch 2022 were 1%, 41%, and 58% with very poor, polluted, and very polluted class, respectively.
The water was not suitable for drinking due to the high concentration of water quality parameters in most locations in the study area. There are many sources of pollution in the region that dump their harmful waste into the river, which led to increase the concentrations of water quality parameters in most locations of study area.
Downloads
References
S. S. Mahapatra, M. Sahu, R. K. Patel, and B. N. Panda, “Prediction of water quality using principal component analysis,” Water Qual. Expo. Heal., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 93–104, 2012.
E. Sánchez et al., “Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watersheds pollution,” Ecol. Indic., vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 315–328, 2007.
S. Water and W. H. Organization, “Water, sanitation and hygiene links to health: facts and figures,” 2004.
I. S. Akoteyon, A. O. Omotayo, O. Soladoye, and H. O. Olaoye, “Determination of water quality index and suitability of urban river for municipal water supply in Lagos-Nigeria,” Eur. J. Sci. Res., vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 263–271, 2011.
N. Al-Ansari, “Management of water resources in Iraq: perspectives and prognoses,” Engineering, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 667–684, 2013.
A. Kibaroglu, “State-of-the-art review of transboundary water governance in the Euphrates–Tigris river basin,” Int. J. Water Resour. Dev., vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 4–29, 2019.
A. Chabuk, Q. Al-Madhlom, A. Al-Maliki, N. Al-Ansari, H. M. Hussain, and J. Laue, “Water quality assessment along Tigris River (Iraq) using water quality index (WQI) and GIS software,” Arab. J. Geosci., vol. 13, no. 14, 2020, doi: 10.1007/s12517-020-05575-5.
C. Fremerey, A. K. Liefländer, and F. X. Bogner, “Conceptions about Drinking Water of 10 th Graders and Undergraduates,” J. Water Resour. Prot., vol. 6, no. 12, p. 1112, 2014.
N. Adamo, N. Al-Ansari, V. K. Sissakian, S. Knutsson, and J. Laue, “Climate change: consequences on Iraq’s environment,” J. earth Sci. Geotech. Eng., vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 43–58, 2018.
S. M. Sadat-Noori, K. Ebrahimi, and A. M. Liaghat, “Groundwater quality assessment using the Water Quality Index and GIS in Saveh-Nobaran aquifer, Iran,” Environ. Earth Sci., vol. 71, no. 9, pp. 3827–3843, 2014.
A. N. Abed, G. Y. Al Kindi, and T. A. Hussain, “Assessment of the Water Quality Index of the Tigris River between the University of Baghdad and Diyala River,” Eng. Technol. J., vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 512–519, 2021.
A. Akkoyunlu and M. E. Akiner, “Pollution evaluation in streams using water quality indices: A case study from Turkey’s Sapanca Lake Basin,” Ecol. Indic., vol. 18, pp. 501–511, 2012.
D. Katyal, “Water quality indices used for surface water vulnerability assessment,” Int. J. Environ. Sci., vol. 2, no. 1, 2011.
A. Chabuk, A. Al-Maliki, N. Al-Ansari, and J. Laue, “Evaluation of the groundwater quality for irrigation: Case study of Hilla district, Babylon Province, Iraq,” in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, vol. 928, no. 2, p. 22056.
N. A. A. L. Naqeeb and S. H. Jazza, “Quality assessment of drinking water by using some Environment Index in Misan Province,” 2020.
J. Sirajudeen and A. R. Vahith, “Applications of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment on Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry, India,” J. Environ. Res. Dev., vol. 8, no. 3, p. 443, 2014.
A. H. M. J. Alobaidy, B. K. Maulood, and A. J. Kadhem, “Evaluating raw and treated water quality of Tigris River within Baghdad by index analysis,” J. water Resour. Prot., vol. 2, no. 7, p. 629, 2010.
B. S. Abed, M. H. Daham, and A. H. Ismail, “Water quality modelling and management of Diyala river and its impact on Tigris River,” J. Eng. Sci. Technol., vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 122–135, 2021.
A. H. Ismail, G. Hassan, and A.-H. Sarhan, “Hydrochemistry of shallow groundwater and its assessment for drinking and irrigation purposes in Tarmiah district, Baghdad governorate, Iraq,” Groundw. Sustain. Dev., vol. 10, p. 100300, 2020.
A. Zowain and A. H. Ismail, “Management of salinity issues in Iraq’s agricultural sector using SWOT analysis,” Eng. Technol. J., vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 644–658, 2015.
A. H. M. J. Alobaidy, M. A. Al-Sameraiy, A. J. Kadhem, and A. A. Majeed, “Evaluation of treated municipal wastewater quality for irrigation,” J. Environ. Prot. (Irvine,. Calif)., vol. 1, no. 03, p. 216, 2010.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Khadeeja G. Sabeeh, Mustafa T. Mustafa , Alhassan H. Ismail , Corina Boncescu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.













