A HOMER-Aided Study for PV System Design and Cost Analysis for a College Campus in Baghdad
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51173/jt.v5i2.722Keywords:
Pilot Study, Hybrid System, Near Zero Energy Building, Lithium Storage Capacities, College CampusAbstract
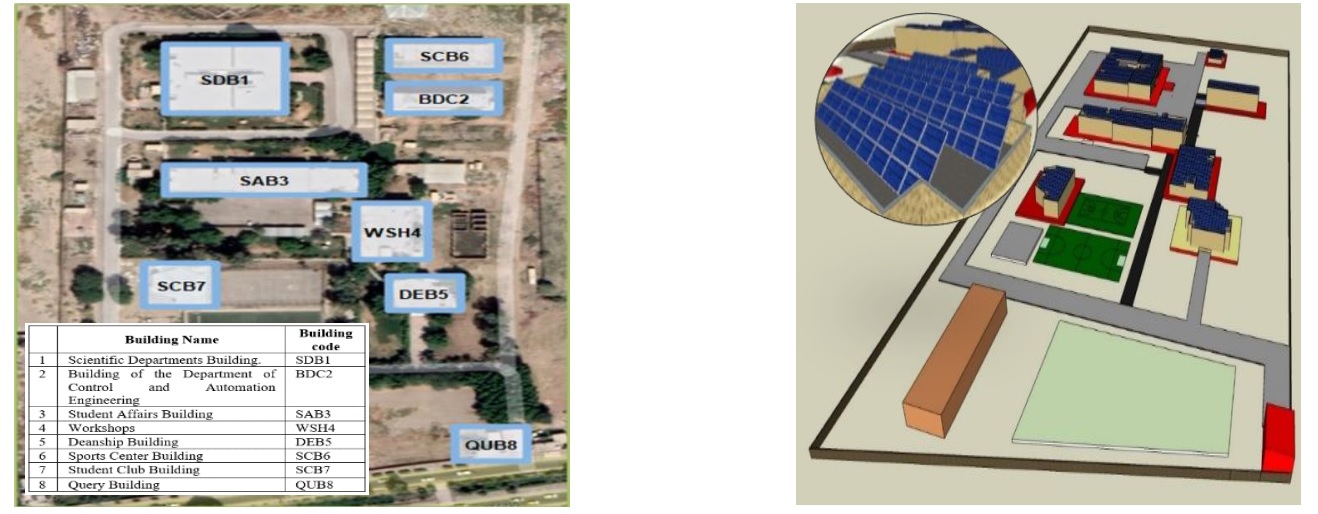
Due to the lack of electric power generation in Iraq and as a step forward to adopting a sustainable campus of the Electrical Engineering Technical College (EETC), Middle Technical University, in Baghdad, Iraq, and the critical demand for energy in our institutions, particularly educational institutions, this pilot study was proposed. The study aims to analyze the adoption of PV solar systems on the campus in the presence and absence of grid power and how that affects our design discussion in the matter of Net Present Cost (NPC), Cost of Energy (COE), Operation Cost, initial cost, power production, fuel consumption, and the annual net consumed energy from the grid. Forty-five different scenarios were analyzed for all possible cases. The existence of backup generators on the campus was also taken into consideration; G1-350kVA and G2-500kVA. The study has two stages. In the first stage, they used a walkthrough energy audit in the (EETC) to estimate the load profile of the campus, while in the second stage, they used HOMER Pro to analyze this data. The results show that adding an on-grid PV system to the campus grid can reduce the COE by 58%, and it is the best scenario when the grid is present, with an NPC, operation cost ($/yr), and initial capital ($) equal to $77,680, $1,460, and $59,018 respectively. When the grid was absent, the winning scenario was using a PV solar system with a 100-kWh lithium battery storage and a converter. Despite that scenario being the best solution, the produced energy cost is 372% higher than the grid energy cost (0.1 $/kWh) in Iraq, with an NPC, operation cost ($/yr.), and initial capital ($) equal to $337,291, $7,855, and 236878 respectively. Finally, both winning scenarios have no generator, and this will have a high impact on the campus environment.
Downloads
References
V. V. Murty and A. Kumar, "Optimal Energy Management and Techno-economic Analysis in Microgrid with Hybrid Renewable Energy Sources," Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 929-940, 2020, doi: 10.35833/MPCE.2020.000273.
C. T. Tsai, T. M. Beza, E. M. Molla, and C. C. Kuo, "Analysis and Sizing of Mini-Grid Hybrid Renewable Energy System for Islands," IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 70013-70029, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2983172.
F. S. Azad, I. Ahmed, S. R. Hossain, and R. A. Tuhin, "HOMER Optimized Off-grid Hybrid Energy System: A Case Study on Rohingya Relocation Center in Bangladesh," in 2019 1st International Conference on Advances in Science, Engineering and Robotics Technology (ICASERT), 3-5 May 2019 2019, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/ICASERT.2019.8934534.
N. Varshney, M. Sharma, and D. Khatod, "Sizing of hybrid energy system using HOMER," International Journal of Emerging Technology Advanced Engineering, vol. 3, no. 6, pp. 436-442, 2013.
G. Shafiullah, A. M. Oo, A. Ali, D. Jarvis, and P. Wolfs, "Economic analysis of hybrid renewable model for subtropical climate," International journal of thermal environmental engineering, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 57-65, 2010.
W. O. Amor, H. B. Amar, and M. Ghariani, "Energetic and cost analysis of two conversion systems connected to the Grid by using Homer pro," International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 926-935, 2015.
L. Ali and F. Shahnia, "Determination of an economically-suitable and sustainable standalone power system for an off-grid town in Western Australia," Renewable Energy, vol. 106, pp. 243-254, 2017/06/01/ 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.12.088.
S. Kumar, P. Upadhyaya, and A. Kumar, "Performance Analysis of Solar Energy Harnessing System Using Homer Energy Software and PV Syst Software," in 2019 2nd International Conference on Power Energy, Environment and Intelligent Control (PEEIC), 18-19 Oct. 2019 2019, pp. 156-159, doi: 10.1109/PEEIC47157.2019.8976665.
Y. Sawle, S. Jain, S. Babu, A. Nair, and B. Khan, "Prefeasibility economic and sensitivity assessment of hybrid renewable energy system. IEEE Access 9: 28260–28271," ed, 2021.
A. Pérez-Santiago, R. Ortiz-Dejesus, and E. I. Ortiz-Rivera, "HOMER: A valuable tool to facilitate the financing process of photovoltaic systems in Puerto Rico," in 2014 IEEE 40th Photovoltaic Specialist Conference (PVSC), 8-13 June 2014 2014, pp. 1467-1470, doi: 10.1109/PVSC.2014.6925192.
S. Bahramara, M. P. Moghaddam, and M. R. Haghifam, "Optimal planning of hybrid renewable energy systems using HOMER: A review," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 62, pp. 609-620, 2016/09/01/ 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.05.039.
K. H. Chua, Y. S. Lim, and S. Morris, "Cost-benefit assessment of energy storage for utility and customers: A case study in Malaysia," Energy Conversion and Management, vol. 106, pp. 1071-1081, 2015/12/01/ 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.10.041.
M. S. Adaramola, M. Agelin-Chaab, and S. S. Paul, "Analysis of hybrid energy systems for application in southern Ghana," Energy Conversion and Management, vol. 88, pp. 284-295, 2014/12/01/ 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.08.029.
L. Q.Ibrahim, A. J. Abid, and A. A. Obed, "Load Performance Analysis via Walkthrough Energy Audit Method: A Case Study for a College Campus in Iraq," presented at The Fourth Scientific Conference for Electrical Engineering Techniques Research (EETR 2022 Electrical Engineering Technical College 2022. [Online]. Available: https://sites.google.com/view/eetr2022/home.
Weatherspark.com [Online] Available: https://weatherspark.com/y/103217/Average-Weather-in-Baghdad-Iraq-Year-Round.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Luqman Q. Ibrahim, Ahmed J. Abid, Adel A. Obed, Ameer L. Saleh, Reheel J. Hassoon

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
















